The Power of COALESCE in SQL: A Complete Guide for Data Professionals
21 de Maio de 2025, 7:10 - sem comentários aindaSQL COALESCE

Introduction
In the world of data management and analytics, dealing with NULL values is a common and often frustrating challenge. Whether you're building reports, performing calculations, or preparing datasets for machine learning, missing values can break queries and distort results. That’s where the COALESCE SQL function comes in — a simple yet powerful tool that every data professional should have in their toolkit.
This guide will walk you through the syntax, use cases, performance tips, and practical examples of the SQL COALESCE function, demonstrating how to utilize it effectively to handle NULL values and optimize your SQL queries.
What Is COALESCE in SQL?
The COALESCE SQL function returns the first non-null value from a list of expressions. It's commonly used to replace NULLs with default values or fallbacks.
Syntax:
COALESCE(expression1, expression2, ..., expression_n)
The function evaluates each expression in order and returns the first one that is not NULL. If all arguments are NULL, the function itself returns NULL.
Why Use SQL COALESCE?
Here are some reasons why SQL COALESCE is widely used:
- Handle missing data: Substitute NULL values with meaningful defaults.
- Simplify case expressions: Replace complex CASE statements with concise syntax.
- Improve data presentation: Ensure consistent and clean results in reports.
- Enhance joins and calculations: Prevent NULLs from affecting aggregate results or calculations.
Real-World Examples of Using COALESCE SQL
Let’s explore a few practical examples to understand how COALESCE SQL works in real scenarios.
- Replace NULL with a Default Value
Imagine a table of users where some entries have NULL values for their phone numbers. You can use COALESCE to display a placeholder text instead.
SELECT
user_id,
COALESCE(phone_number, 'Not Provided') AS contact_info
FROM
users;
Result: Users without a phone number will now show “Not Provided” instead of NULL.
- Fallback Through Multiple Columns
Suppose you’re working with a product inventory where a product could have a local price, regional price, or global price. You can use SQL COALESCE to pick the best available one.
SELECT
product_id,
COALESCE(local_price, regional_price, global_price, 0) AS final_price
FROM
products;
This returns the first available price, ensuring that no product ends up with a NULL value.
- Using COALESCE in Aggregations
Let’s say you're calculating the average of a column that has NULLs. Without handling NULLs, your results might be skewed.
SELECT
AVG(COALESCE(rating, 0)) AS avg_rating
FROM
product_reviews;
This treats NULL ratings as zeroes, allowing for more inclusive calculations.
- COALESCE with Joins
When joining tables, you might want to use data from either side of the join.
SELECT
COALESCE(a.customer_name, b.guest_name) AS name
FROM
orders a
LEFT JOIN
guest_orders b ON a.order_id = b.order_id;
If customer_name is NULL (perhaps from a missing join), the query will fall back to guest_name.
COALESCE vs ISNULL vs NVL
Different SQL dialects have similar functions:
- COALESCE: Standard SQL, works across most databases.
- ISNULL: Used in SQL Server.
- NVL: Used in Oracle.
While ISNULL and NVL work similarly for two arguments, COALESCE is more flexible because it can take multiple arguments and follows standard SQL behavior.
Best Practices When Using COALESCE SQL
- Be consistent: Use COALESCE to create cleaner, more predictable outputs in reports and dashboards.
- Avoid logic errors: Ensure data types in all arguments are compatible to prevent implicit conversion issues.
- Use in SELECT, WHERE, ORDER BY: COALESCE is versatile and works in various SQL clauses.
- Watch out for performance: When used heavily in large datasets, test performance and consider indexing or filtering data beforehand.
Conclusion
The COALESCE SQL function is a powerful asset for any data analyst, engineer, or developer working with relational databases. It helps you handle NULL values gracefully, simplify query logic, and produce cleaner, more reliable results.
Whether you're formatting output for a report, calculating metrics, or managing fallbacks across multiple columns, this SQL COALESCE guide should help you confidently write better, cleaner SQL.
If you're aiming to master SQL, understanding COALESCE is a key milestone — and this might just be the best C++ tutorial for managing NULLs that you've seen yet.
Understanding Binary Search Tree Traversals: Inorder, Preorder, Postorder
3 de Maio de 2025, 7:22 - sem comentários aindaBinary Search Tree
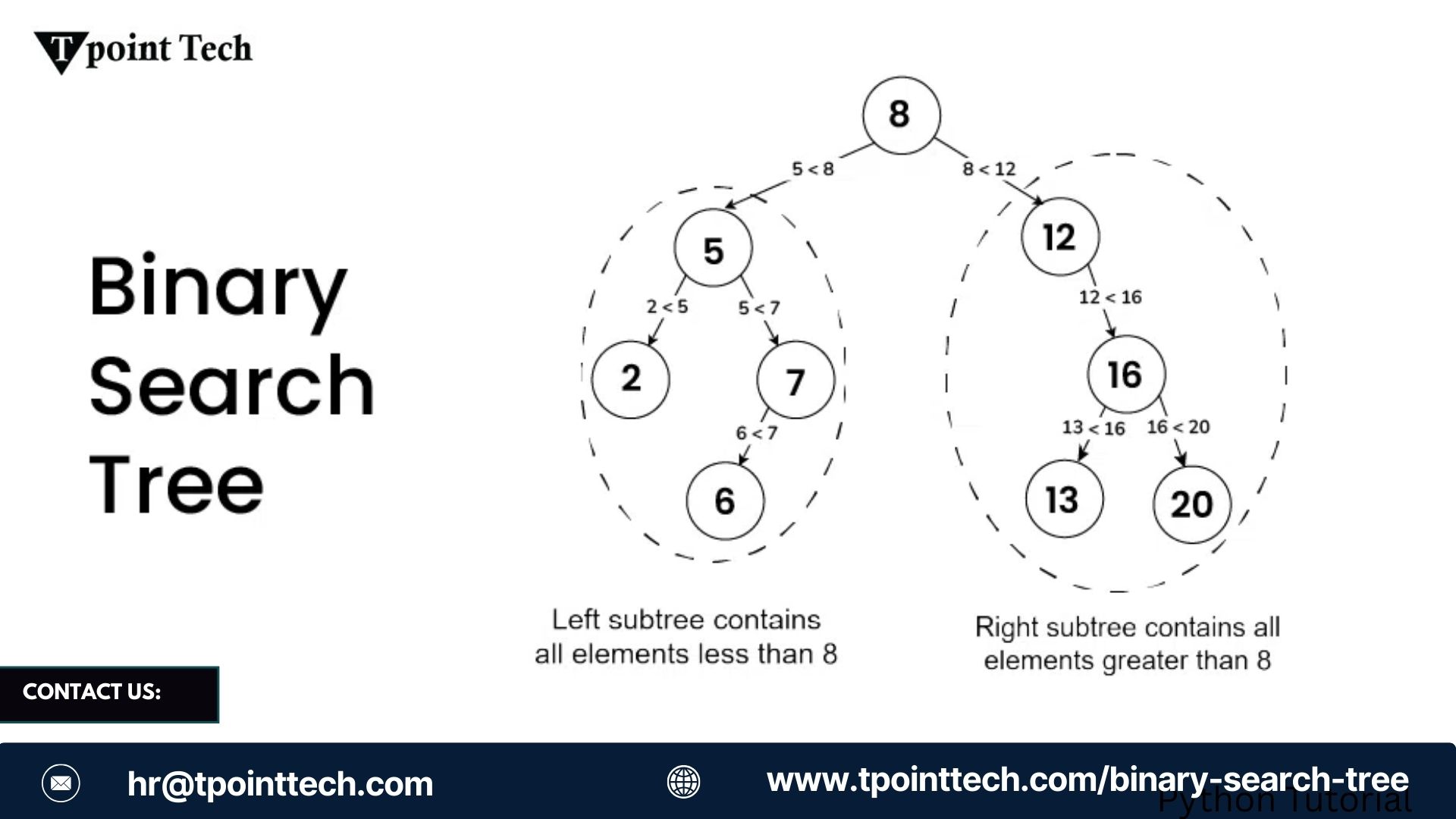
Introduction
A Binary Search Tree (BST) is a specialized type of Binary Tree that maintains sorted order among its elements, making it extremely useful for operations like search, insertion, and deletion. In a BST, each node has at most two children: the left child, which contains values less than the node, and the right child, which contains values greater than the node. To effectively work with binary trees, especially for algorithms and data manipulation, understanding tree traversals is essential.
Tree traversal is the process of visiting every node in the tree exactly once in a specific order. The three primary types of depth-first traversal techniques are Inorder , Preorder , and Postorder . Each method follows a different sequence to process the nodes, and they serve different purposes depending on the application.
1. Inorder Traversal (Left → Root → Right)
In inorder traversal , we visit the left subtree first, then the root node, and finally the right subtree. This traversal is particularly important in a Binary Search Tree because it returns the node values in sorted (ascending) order .
Algorithm:
Inorder(node):
if node is not null:
Inorder(node.left)
Visit(node)
Inorder(node.right)
Example:
Consider the following Binary Search Tree:
8
/ \
3 10
/ \ \
1 6 14
/ \ /
4 7 13
Inorder Traversal of this tree yields:
1, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8, 10, 13, 14
This output is in sorted order, illustrating why inorder traversal is commonly used to retrieve data from a BST.
2. Preorder Traversal (Root → Left → Right)
In preorder traversal , we visit the root node first, then traverse the left subtree, followed by the right subtree. This method is especially useful for creating a copy of the tree or saving its structure.
Algorith
Preorder(node):
if node is not null:
Visit(node)
Preorder(node.left)
Preorder(node.right)
Example:
Using the same Binary Search Tree:
Preorder Traversal yields:
8, 3, 1, 6, 4, 7, 10, 14, 13
Preorder traversal starts at the root and descends left before going right. This traversal can be used to serialize a binary tree into a file or memory.
3. Postorder Traversal (Left → Right → Root)
In postorder traversal , we traverse the left subtree first, then the right subtree, and finally the root node. This traversal is useful for deleting or freeing nodes , because it processes children parents before.
Algorithm:
Postorder(node):
if node is not null:
Postorder(node.left)
Postorder(node.right)
Visit(node)
Example:
Postorder Traversal yields:
1, 4, 7, 6, 3, 13, 14, 10, 8
In postorder traversal, the root is visited last, making it ideal for operations where the subtrees need to be handled before the parent node (eg, in memory deallocation).
Why Tree Traversals Matter
Understanding these traversal methods is crucial when working with any Binary Tree , not just BSTs. Each traversal technique solves different kinds of problems:
-
Inorder : Best for retrieving sorted data from a Binary Search Tree .
-
Preorder : Useful for copying a tree or converting it into a different format.
-
Postorder : Ideal for deletion, evaluation of expressions, or memory cleanup.
For example, in expression trees (a specialized type of binary tree), these traversals correspond to different notations:
-
Preorder → Prefix notation
-
Inorder → Infix notation
-
Postorder → Postfix notation
How to Implement Tree Traversals in Code (Python Example)
Here's how you can implement all three traversals using a simple Nodeclass:
class Node:
def __init__(self, value):
self.value = value
self.left = None
self.right = None
def inorder(node):
if node:
inorder(node.left)
print(node.value, end=" ")
inorder(node.right)
def preorder(node):
if node:
print(node.value, end=" ")
preorder(node.left)
preorder(node.right)
def postorder(node):
if node:
postorder(node.left)
postorder(node.right)
print(node.value, end=" ")
You can construct the Binary Search Tree manually and call these functions to see each traversal in action.
Conclusion
Understanding Binary Search Tree traversals is foundational for anyone learning data structures and algorithms. Whether you're performing searches, storing data efficiently, or managing system resources, knowing how to properly traverse a binary tree will make you a more effective programmer.
By mastering inorder , preorder , and postorder traversals, you're not just learning how to walk through a tree—you're gaining powerful tools to solve real-world problems in software engineering, data processing, and algorithm design.
Optimizing Data Processing with Efficient Use of SAS Operators
2 de Maio de 2025, 8:18 - sem comentários ainda
SAS Operators

Introduction
Efficient data processing is at the heart of any analytics workflow, and the SAS programming language is widely used for its powerful data manipulation capabilities. In this article, we explore how to optimize your data processing tasks using SAS operators . If you're new to SAS, don't worry—we'll start with a quick SAS introduction and build up to more advanced concepts that can help you write cleaner, faster, and more efficient code.
SAS Introduction: The Basics
SAS (Statistical Analysis System) is a software suite developed by SAS Institute for advanced analytics, data management, and business intelligence. It is widely used in industries such as healthcare, finance, government, and academia for data analysis and reporting.
One of the first things you'll learn in any SAS introduction is that data in SAS is handled in two major phases:
-
DATA Step – where data is read, manipulated, and prepared.
-
PROC Step – where data is analyzed or presented using built-in procedures.
Within the DATA step , SAS operators play a crucial role in manipulating and transforming data. Mastering these operators is essential for writing efficient and readable SAS programs.
What Are SAS Operators?
SAS operators are symbols or keywords used to perform mathematical, logical, comparison, and character-based operations. They are similar in function to operators in other programming languages but have some unique features suited to SAS's data processing framework.
Operators can be grouped into the following main categories:
-
Arithmetic Operators
-
Comparison Operators
-
Logical Operators
-
Character Operators
-
Special Operators
Optimizing Data Processing with SAS Operators
Let's now look at how you can use each type of SAS operator efficiently to improve data processing.
1. Arithmetic Operators
These include +, -, *, /, and **(exponentiation). While simple, using them effectively can streamline data calculations.
Example:
data work.sales;
set work.sales_data;
TotalRevenue = UnitsSold * PricePerUnit;
DiscountedRevenue = TotalRevenue - (TotalRevenue * DiscountRate);
run;
Optimization Tip:
Avoid unnecessary recalculations by computing complex expressions once and storing them in variables. This reduces computation time, especially for large datasets.
2. Comparison Operators
These include =, >, <, >=, <=, and ^=(not equal). Comparison operators are commonly used in conditional logic, such as in IFstatements.
Example:
if Age >= 65 then Senior = 1;
else Senior = 0;
Optimization Tip:
Use comparison operators in combination with logical operators to simplify complex conditional checks.
3. Logical Operators
Logical operators are AND, OR, and NOT. These are essential for filtering data efficiently.
Example:
if Gender = 'F' and Age > 30 then output;
Optimization Tip:
Arrange conditions with the most likely true cases first in IFstatements, as SAS stops evaluating once the outcome is determined. This is known as short-circuit evaluation .
4. Character Operators
The main character operator is the concatenation operator ( ||), used to join strings.
Example:
FullName = FirstName || ' ' || LastName;
Optimization Tip:
Use the CATX, CATS, or CATTfunctions when dealing with multiple strings to handle missing values and delimiters more gracefully.
5. Special Operators
Special operators like IN, BETWEEN, and LIKEare extremely useful for filtering data succinctly.
Example:
if ProductType in ('Book', 'Magazine', 'Journal') then MediaType = 'Print';
Optimization Tip:
Use INinstead of multiple OR conditions. It improves code readability and may also lead to slight performance gains.
Common Efficiency Mistakes to Avoid
-
Redundant Calculations : Repeating the same arithmetic operation in multiple statements.
-
Complex Nested IFs : Break down logic or use
SELECT-WHENfor clarity and efficiency. -
Unfiltered Dataset Access : Use WHERE clauses and logical operators to limit the number of records processed.
Putting It All Together
Efficient use of SAS operators allows you to write cleaner, more concise, and faster-executing code. For example, consider this well-optimized DATA step:
data work.clean_data;
set work.raw_data;
if Age >= 18 and Income > 25000 and Country in ('USA', 'CAN', 'UK');
FullName = catx(' ', FirstName, LastName);
Eligibility = (CreditScore > 700 and NOT missing(JobStatus));
run;
This code filters data at the earliest possible step, avoids redundancy, and uses SAS functions along with operators for optimized string handling.
Conclusion
In this SAS introduction , we explored how efficient use of SAS operators —arithmetic, logical, comparison, and special—can significantly improve your data processing workflows. Whether you're calculating new variables, filtering rows, or building complex conditions, the right use of operators can enhance both performance and readability.
By mastering SAS operators, you not only become a more effective programmer but also gain the skills needed to handle large and complex datasets with precision and speed. Make these best practices part of your everyday coding, and you'll soon notice a substantial improvement in your SAS programming efficiency.

